Scope and sequence (F–10)
Learning programs to support implementation
Sequenced topics that could be used in teaching the Australian Curriculum Digital Technologies curriculum to address the content descriptions of the curriculum. The Scope and sequence has been updated to support teachers to implement AC:DT V9.0.
Select a topic
Choose a combination of units that suits your students and context.
Cycle one (Foundation)
Cycle one (Foundation)
| Jan | Jun | Dec | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Representing data
Overview
This unit introduces students to exploring how data – such as a picture, object or symbol – can be used to communicate an idea or observation. They represent data with familiar objects, and identify the features that can help us differentiate one object from the other.
Achievement standards
By the end of Foundation students show familiarity with digital systems and use them for a purpose. They represent data using objects, pictures and symbols and identify examples of data that is owned by them.
Australian Curriculum
Content descriptions
Digital systems AC9TDIFK01
Data representation AC9TDIFK02
Related content and General capabilities
Mathematics: Statistics AC9MFST01
Digital Literacy: Practising digital safety and wellbeing, Managing and operating
This topic enables students to
- explain how an object, picture or symbol stands for an idea or observation
- draw and display pictures to represent our daily activities
- compare representations and identify the commonly used features that make them easy to recognise.
Watch this video for a quick overview of the unit and how to use its resources with your students.
Assessment View assessment advice
Use the work sample Data is all around us and associated task to assess your students’ understanding and knowledge related to representing data using digital systems.
Rubric: Data representation
| Knowledge of data representation | with guidance, can identify types of data | can identify types of data and name them, such as picture, symbol or object | can identify types of data and name them, such as picture, symbol or object, and explain what they represent | can identify types of data and name them and explain what they represent and why we might use that representation |
| Demonstrates ways to represent data | with guidance, represents data using a picture, symbol or object | demonstrates the use of pictures, symbols or objects to represent ideas or actions | demonstrates the use of pictures, symbols or objects to represent ideas or actions, discussing the features that make them easily recognisable | demonstrates the use of pictures, symbols or objects to represent ideas or actions, discussing the features that make them easily recognisable and justifies their choice |
Unit sequence
This topic offers 2 sequential units
Unit 1
Representing ideas and actions
Students represent familiar objects; identify the features that can help us differentiate one from the other.Unit 2
Representing data we collect
Students represent data they collect about familiar experiences and events.Representing ideas and actions
What is this about?
Representing data involves using symbols, visuals or audio to convey information. This can include images, emojis or icons to communicate ideas or observations. For instance, emojis can express emotions, and symbols can depict weather forecasts or observations. Representation is an abstraction of an observation, capturing and expressing information through symbols, visuals or other forms to convey meaning. For example, the U shape represents a happy person even though it is only an abstract representation of a smile, not even a whole person.
Content description
Recognise and explore digital systems (hardware and software) for a purpose AC9TDIFK01
Represent data as objects, pictures and symbols AC9TDIFK02
This sequence enables students to:
- explain how an object, picture or symbol stands for an idea or observation
- draw and display pictures to represent our daily activities
- compare representations and identify the commonly used features that make them easy to recognise.
Resources to include
Resources to introduce
Foundation What is data?
Use this slide presentation to explain the term ‘data’.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify ways in which data is represented.

Foundation Who is in your family?
Use this task to discuss ways to represent data about your family.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- collect data about themselves, including data that is owned by them
- represent data as images, symbols or pictures.

Resources to develop and consolidate learning
-

Emoji time!
Find out more -

Can an AI recognise what you are drawing?
Find out more -

Is it a pig or dog?
Find out more -

Using visual schedules
Find out more
Foundation Emoji time!
Explore the use of emojis to represent feelings.
Requires
- print game cards (enough for students in small groups)
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- describe the key facial features that help us recognise a person’s emotions
- draw and recognise different faces that represent an emotion such as sad, happy or angry.

Foundation Can an AI recognise what you are drawing?
This lesson provides an opportunity to incorporate representation of data using a relevant context being studied in the classroom.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- describe the key features of objects that help us recognise an object
- draw objects, focusing on the features that make them recognisable.

Foundation Is it a pig or dog?
Use this take-home activity to explore data representation.
Requires
- printed worksheet
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- describe the key features that help us recognise an animal
- draw and recognise different animals representing their key features.

Foundation Using visual schedules
Create a visual representation of the class schedule and routines. A visual schedule, such as a timetable, is a visual representation of what activities will occur and in what sequence.
Requires
- a sheet of paper or whiteboard to list classroom activities
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- describe the daily schedule of activities that occur in a sequence
- represent daytime activities as images, symbols or pictures.

Resources to extend integrate learning
-

Creating a visual guide to packing the school bag
Find out more -

All about me
Find out more -

Can AI guess your emotion?
Find out more -

Robot dance
Find out more
Foundation Creating a visual guide to packing the school bag
This is a take-home activity to be completed as a family task. Students use pictures to represent data.
Requires
- printed worksheet or electronic version of slides
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- use a common digital system for a particular purpose
- recognise data represented as images.

Foundation All about me
Discuss ways to represent each type of data students record about themselves.
Requires
- printed worksheet
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- collect data about themselves including data that is owned by them
- represent data as images, symbols or pictures.

Foundation Can AI guess your emotion?
Use this lesson to explore using emojis to represent feelings or emotions.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display teachable machine website
- access to printed emojis
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- describe the key facial features a person's emotions
- draw and recognise different faces that represent an emotion such as sad, happy or angry.
Foundation Robot dance
Use this take home task to discuss ways to represent dance moves.
Requires
- printed worksheet
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- represent dance moves using pictures.

Professional learning
Foundation Data representation
Use this infographic to explore ways to represent data for your year level.
Requires
- 30 minutes
Representing data we collect
What is this about?
Through Digital Technologies and Mathematics (Statistics), students have opportunities to explore different ways that data can be acquired and recorded; for example, using a table to record facts about themselves, using a tablet to take photographs of plants in the local area, or exploring their lunchbox to look for patterns in data.
Content descriptions
Recognise and explore digital systems (hardware and software) for a purpose AC9TDIFK01
Represent data as objects, pictures and symbols AC9TDIFK02
This sequence enables students to:
- conduct a simple survey to collect responses
- record the survey responses using tally marks, numbers or pictures
- represent data as images, symbols or pictures.
Resources to include
Resources to introduce
Foundation All about me
Discuss ways to represent each type of data students record about themselves.
Requires
- printed worksheet
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- collect data about themselves including data that is owned by them
- represent data as images, symbols or pictures.

Foundation Organising information
Use the context of organising information to explore ways to represent data.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- organise data into groups
- represent data using images, symbols and text.
Resources to develop and consolidate learning
Foundation Data collection and representation: What's in your lunchbox? (Years F-2)
The type of fruits and vegetables in school lunchboxes or those eaten at Crunch&Sip or fruit break time can provide a good source of data for a classroom investigation.
Requires
- school lunchboxes
- devices with camera such as an iPad
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- organise data into groups
- represent data using images, symbols and text.

Resources to extend an integrate learning
Foundation Data detective
With support, students conduct a simple survey to collect, organise and present data. In doing so, they demonstrate their understanding of how to use patterns to represent data symbolically.
Requires
- printed worksheet
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- conduct a simple survey to collect responses from friends
- record the survey responses using tally marks, numbers or pictures
- organise the data using tables and lists.

Foundation Seasonal walk
Students explore their local area to collect and represent data about the plants and animals they observe.
Requires
- printed worksheet
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- draw and display pictures to represent our daily activities
- compare representations and identify the commonly used features that make them easy to recognise.

Using digital systems safely
Overview
This unit introduces students to common digital systems and builds an understanding of the role hardware and software play as students use digital systems for a purpose. They also learn about how to practise being safe users of digital systems.
Achievement standards
By the end of Foundation students show familiarity with digital systems and use them for a purpose. They represent data using objects, pictures and symbols and identify examples of data that is owned by them.
Australian Curriculum
Content descriptions
Digital systems AC9TDIFK01
Privacy and security AC9TDIFP01
Data representation AC9TDIFK02
Related content and General capabilities
Digital Literacy: Practising digital safety and wellbeing, Managing and operating
This topic enables students to
- identify some common digital systems
- describe and use a common digital system and its particular purpose
- describe examples of hardware and software.
Watch this video for a quick overview of the unit and how to use its resources with your students.
Assessment View assessment advice
Using the work sample We live in a digital world students will investigate a variety of digital systems that are used in their home and school environments. They will identify the specific features of these and outline how they are used in everyday life.
Rubric: Common digital systems
| Knowledge of common digital systems | with guidance can identify some common digital systems | shows understanding of common digital systems and describes one digital system and its purpose | shows understanding of common digital systems and their purpose, and can identify features and some hardware and software | shows understanding of common digital systems, identifies their features, purpose and the role of hardware and software |
| Demonstrates use of common digital systems | has limited capacity to demonstrate the use of a common digital system | demonstrates the use of a common digital system and can partly describe its purpose | demonstrates the use of at least one common digital system and can clearly describe its purpose | selects a digital system for a given purpose, demonstrates its use and justifies their choice |
| Creates a model of common digital systems | the model has minimal resemblance to a common digital system | the model has recognisable features of a common digital system | the model has clearly recognisable features of a common digital system | the model has clearly recognisable features of a common digital system and the student explains the different parts |
Rubric: Personal information
| Knowledge of personal information | has a limited understanding of personal information | shows understanding of personal information and gives some examples of data that is personal | shows understanding of personal information and gives some examples of data that is personal, and explains why it is important to protect this information and keep it safe | shows understanding of personal information, gives examples of data that is personal, and explains why it is important to protect this information and keep it safe. They identify where personal data could be made visible when using digital systems |
| Uses digital systems, keeping their personal information safe | uses digital systems but needs to be reminded to keep their personal information safe | uses digital systems and describes some ways to keep their personal information safe | uses digital systems and describes ways to keep their personal information safe | uses digital systems safely and describes relevant strategies – including the importance of a trusted adult – to keep their personal information safe when asked to give their personal information |
Unit sequence
This topic offers 3 sequential units
Unit 1
Common digital systems we use
Students explore common digital systems and use them for a purpose.Unit 2
Make a model of a digital system
Students make a model of a digital system to apply their understanding of digital systems.Unit 3
Safe use of digital systems
Students identify ways to stay safe when using digital systems and learn about how to keep their personal information safe.Common digital systems we use
What is this about?
A computer is a common digital system. Tablets, laptops and smartphones are also digital systems.
The digital system uses hardware and software components to enable a user to complete specific tasks.
Hardware refers to the physical parts of the computer that you can touch. A desktop computer includes the case (or tower), monitor, keyboard and mouse. The software refers to the applications that make the computer work and tell it what to do. These might include word-processing and presentation software, a drawing program, photo editing, video playing and other applications.
Content description
Recognise and explore digital systems (hardware and software) for a purpose AC9TDIFK01
This sequence enables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe and use a common digital system and its particular purpose
- describe examples of hardware and software.
Resources to include
Resources to introduce
-

Basic parts of a computer
Find out more -

What is a computer system?
Find out more -

Do computers have a memory?
Find out more
Foundation Basic parts of a computer
Use this tutorial to explain the basic parts of a computer and the important role they play.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems describe a common digital system and its particular purpose.

Foundation What is a computer system?
Use this guide to explain hardware (the physical parts of the computer) and software (the programs that run on a computer).
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- describe examples of hardware and software.

Foundation Do computers have a memory?
Use this resource to discuss how computer memory helps us save and store information.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems.

Resources to develop and consolidate learning
-

Using a computer to write
Find out more -

How can you make digital art?
Find out more -

How can we make digital pictures move?
Find out more -

What are digital photos and videos?
Find out more -

How do we communicate online?
Find out more
Foundation Using a computer to write
Use this resource to discuss how computer helps us write.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and it's particular purpose.
Foundation How can you make digital art?
Use this resource to discuss how computer helps us to create digital art.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose.

Foundation How can we make digital pictures move?
Use this resource to discuss how computers help us to create simple animations.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose.

Foundation What are digital photos and videos?
Use this resource to discuss how we use devices with cameras to take digital photographs and video.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose.

Foundation How do we communicate online?
Use this resource to discuss how we communicate online.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose.

Resources to apply and extend learning
-

Creating a visual guide to packing the school bag
Find out more -

We're going on a computer hunt
Find out more -

Digital learning: Ideas to try
Find out more
Foundation Creating a visual guide to packing the school bag
This is a take-home activity to be completed as a family task.
Requires
- printed slides, one set per student, or provide access to downloadable slides
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- use a common digital system for a particular purpose
- recognise data represented as images.

Foundation We're going on a computer hunt
This is a take-home activity to be completed as a family task.
Requires
- printed slides, one set per student, or provide access to downloadable slides
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose.

Foundation Digital learning: Ideas to try
Provides examples of ways to use digital devices for a purpose.
Requires
- resources required depend on the activity chosen
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose.

Background and professional learning
-

What is a digital system and how do digital systems help us? (Years Foundation)
Find out more -

Privacy and security infographic (F-10)
Find out more
Foundation What is a digital system and how do digital systems help us? (Years Foundation)
Use this resource as a guide to include digital systems in your teaching program.
Suggested time
30 minutes
Foundation Privacy and security infographic (F-10)
Explore privacy and security for your Year band.
Suggested time
30 mins
Further reading and professional learning
Make a model of a digital system
What is this about?
A computer is a common digital system. Tablets, laptops and smartphones are also digital systems. Making a model of a digital system enables students to apply their understanding of digital systems. Presenting the task to solve a problem, such as taking a selfie and sending it to a relative, connects the digital system with a purpose. Model how to identify the hardware and software and any peripheral devices they may add to their digital system to complete a specific task.
Content descriptions
Recognise and explore digital systems (hardware and software) for a purpose AC9TDIFK01
Represent data as objects, pictures and symbols AC9TDIFK02
This sequence enables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose
- create a model of a digital system
- recognise data represented in common digital systems.
Resources to include
Resources to introduce
-

Computer basics - Basic parts of a computer
Find out more -

Using a keyboard , mouse and touchpad
Find out more -

Making a keyboard
Find out more
Foundation Computer basics - Basic parts of a computer
Use this resource to teach about the basic parts of a computer.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose.

Foundation Using a keyboard , mouse and touchpad
Use this resource to discuss parts of a digital system and what they do.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display website
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose.

Foundation Making a keyboard
Students build their own computer keyboard and learn about alphabets, numbers and symbols.
Requires
- print handout (one per student)
- stiff card to attach printed keyboard to (optional)
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose
- recognise data represented as letters, numbers and symbols.
Resources to develop and consolidate learning
Foundation How to make a Play-Doh iPad tablet
This video provides an overview of how students might create a model of a tablet using Play-Doh.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display video
- Play-Doh or similar material and recycled materials
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose.

Resources to extend and integrate learning
Foundation My first computer
Design your own computer. Includes relevant handouts.
Requires
- markers, recycled materials, scissors, glue
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose
- identify software and what it can be used for.
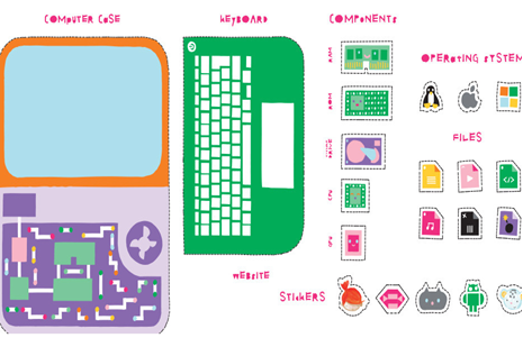
Foundation Creating a digital system
Provide this take-home activity to be completed as a family task.
Requires
- markers, recycled materials, scissors, glue
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose
- identify software and what it can be used for.

Safe use of digital systems
What is this about?
There are many situations, connected to the internet, in which people are asked for their personal information. Personal information can be used to identify a particular person and care must be taken when providing this information. It is potentially dangerous for strangers to have your personal information. Young children must check with a trusted adult before sharing any personal information online.
Content description
Recognise and explore digital systems (hardware and software) for a purpose AC9TDIFK01
Identify some data that is personal and owned by them AC9TDIFP01
This sequence enables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe a common digital system and its particular purpose
- identify ways to stay safe when using digital systems
- describe their personal information (data that is personal and owned by them)
- identify who they would ask for help with being safe online.
Resources to include
Resources to introduce
-

How can you be safe online?
Find out more -

How to keep our personal information private
Find out more -

Under lock and key
Find out more
Foundation How can you be safe online?
Use this resource to discuss what can go wrong when we go online.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display resource
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe what can go wrong when we go online
- describe ways to stay safe online.

Foundation How to keep our personal information private
Use this resource to discuss personal information and how we protect it.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display resource
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe their personal information
- describe ways to stay safe online.
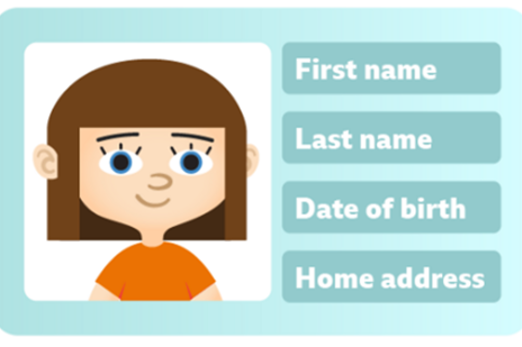
Foundation Under lock and key
Use this activity to help students understand the concept of personal information and why it’s important to protect personal information that identifies you.
Requires
- one printed worksheet per student
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- describe their personal information
- describe ways to stay safe online.

Resources to develop and consolidate learning
Foundation Ask for help
This activity helps students to recognise an unsafe situation when using digital systems and explore help-seeking strategies.
Requires
- printed game card (enough for students in small groups)
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe their personal information
- identify who they would ask for help with being safe online.

Foundation How our class stays safe online
This resource can be used in the classroom to teach students aged 5 to 8 years about safe online behaviour. It includes discussion questions, a poster and guidelines about how to create a tech agreement.
Requires
- downloadable posters
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- describe their personal information
- describe ways to protect their personal information and stay safe online.

Resources to extend and integrate learning
Foundation Mighty Heroes student page
Use these brief videos to learn how to be safer online.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display video
Suggested time
1 hourEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe their personal information
- describe ways to protect their personal information.

Foundation How to be kind online
Use this online resource to discuss ways to stay safe online.
Requires
- internet access
- computer and interactive whiteboard to display video
Suggested time
30 minutesEnables students to:
- identify some common digital systems
- describe what it means to be kind online
- describe ways to stay safe online.

Background and professional learning
Foundation Curriculum connections: Online safety
Use this resource to learn more about curriculum connections to online safety.
Suggested time
30 minutes









































