Binary

What is it?
The binary number system is a base-2 number system. This means it only has two numbers: 0 and 1. All information in a computer (words, pictures, movies, sound) is stored and transmitted as sequences of bits, or binary digits.
A bit is a single piece of data which can be thought of as either zero or one. Each binary number is made up of bits, for example, the number 1010 is made of 4 bits. When you have 8 bits altogether, this is known as a byte. A byte may look like the number 01000100 and in this case represents the letter 'D'.
Australian Curriculum definition
Binary
A use of two states or permissible values to represent data, such as ON and OFF positions of a light switch or transistors in a computer silicon chip that can be in either the electrical state of ON or OFF.
Binary data are typically represented as a series of single digits referred to as binary digits (or bits) due to each taking on the value of either 0 or 1. The image below shows how a dashed line might be represented in binary.

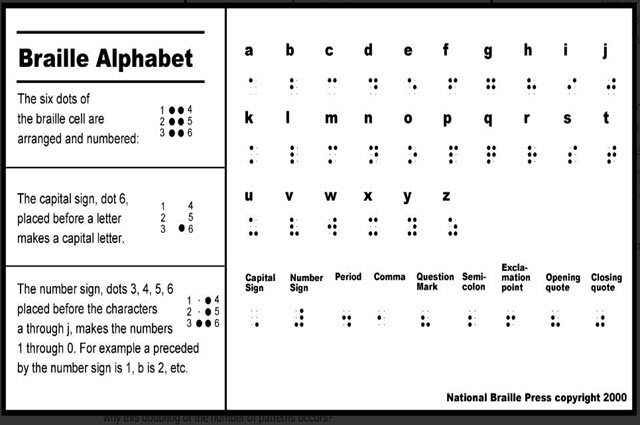
CS Field Guide: Data representation
This chapter is about some of the different methods that computers use to code different kinds of information in patterns of bits, and how this affects the cost and quality of what we do on the computer.

James May's 'What are binary numbers?' (video)
James May asks: 'What are binary numbers, and why does my computer need them?'
How to teach it
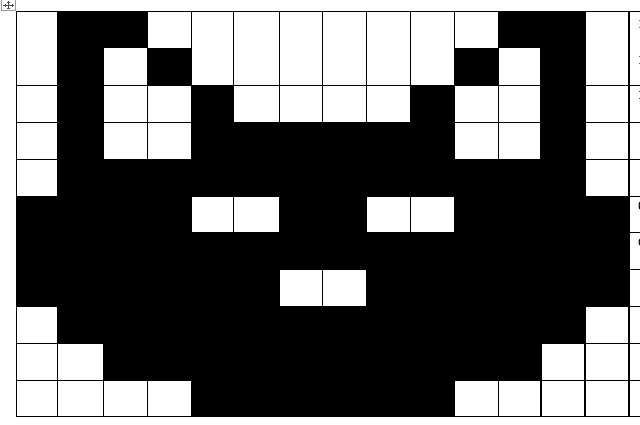
Using binary to create on/off pictures
Students develop an understanding of how computers store and send digital images and they are able to represent images in a digital format.

In this sequence students learn how the binary number system works and how text can be represented using binary numbers. Students learn one of the representations of the standard English alphabet used by computers. They also look at how the same concepts apply to non-text data and analyse the effectiveness of some binary representation techniques to various types of data.

This short sequence focuses on what a binary number is, what a decimal number is (revision), why binary numbers are important in digital systems, and how to read and understand a binary number.
Use these activities with your students to explore how a computer figures out if an error has occurred in stored and transmitted data.
Use these activities with your students to explore how computers use just two symbols, zero and one, to represent information.
CS Unplugged: Modems unplugged
This activity involves listening to songs and finding hidden messages based on the same principle as a modem. Also suitable for upper primary students.
CS Unplugged: Image representation
Use these activities with your students to explore how computers store and transmit data to create a black-and-white image. Also suitable for lower secondary students.
This unit explores the technical challenges and questions that arise from the need to represent digital information in computers and transfer it between people and computational devices.
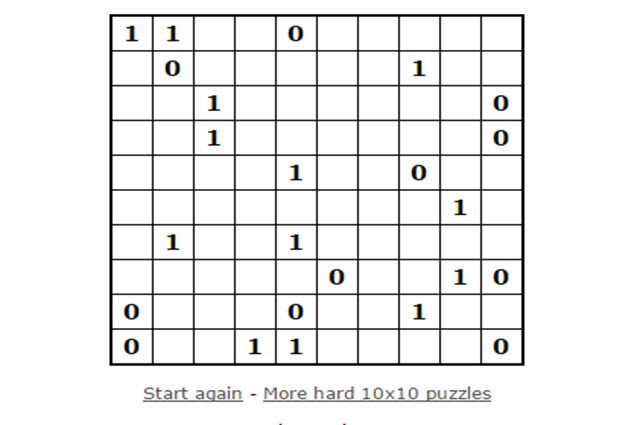
The binary puzzle is a new and challenging logic puzzle that students can solve by reasoning. Only zeros and ones occur in the puzzle, but this turns out to be more complicated than it first seems.
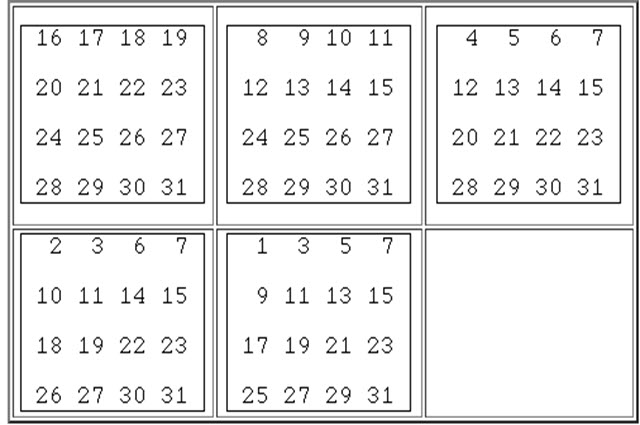
This activity uses binary numbers as a way of identifying the magic number.

ACARA: Binary work samples
Students were introduced to whole numbers using a CS Unplugged video and unplugged group activities. Students completed a worksheet to assess their understanding of binary numbers.

Years 5–6: Representing data in digital systems
This unit explores binary numbers through pixel-based image creation to help students understand the purpose and functionality of binary.

This unit introduces students to the binary system of ones and zeros used by digital technology to store and process numbers. They also learn how text, images and sound can be stored this way.
