Digital systems

What is it?
The term digital system refers to elements such as hardware, software and networks and their use. There may be many different components that make up one system; for example, a computer has a central processing unit, a hard disk, keyboard, mouse, screen etc. A peripheral device is a digital component that can be connected to a digital system, for example, a digital camera or printer.
Australian Curriculum definition
Digital system
Digital hardware and software components (internal and external) used to transform data into a digital solution. When digital systems are connected, they form a network. For example:
- a smartphone is a digital system that has software (apps, an operating system), input components (for example, touch screen, keyboard, camera and microphone), output components (for example, screen and speakers), memory components (for example, silicon chips, solid state drives), communication components (for example, SIM card, wi-fi, bluetooth or mobile network antennas), and a processor made up of one or more silicon chips.
- a desktop computer with specific software and hardware components for dairy farming. The computer is connected via cables to milking equipment and via wi-fi to sensors that read tags on the cows. Through these hardware components the software records how much milk each cow provides. Such systems can also algorithmically control attaching milking equipment to each cow, providing feed and opening gates.

This website features over 30 activities on data, algorithms, procedures, intractability, cryptography, and interacting with computers and community.

Students explore elements of a digital system, including hardware, software and some commonly used peripheral devices. They find out how these elements work together.

Using four inventions from 1985, this lesson sequence explores the impact of innovation, supporting circumstances, how individuals contribute to change, and the importance of addressing benefits as well as risks in the development of new systems.
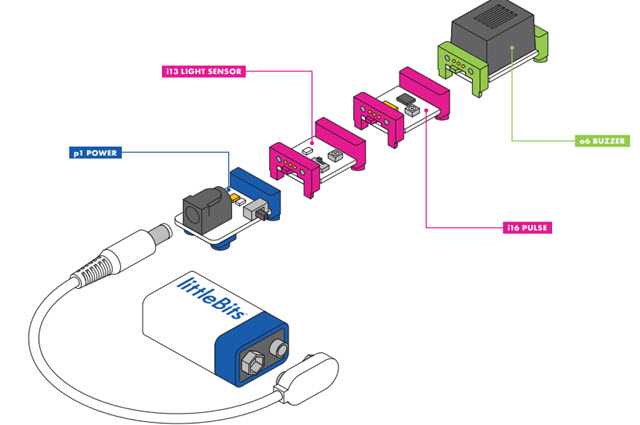
Students explore aspects of animal adaptation prior to applying their knowledge to construct their own digital creature using littleBits electronic sets.

With a focus on input devices, students are encouraged to explore the possibilities and new types of functionality enabled by these technologies over time.
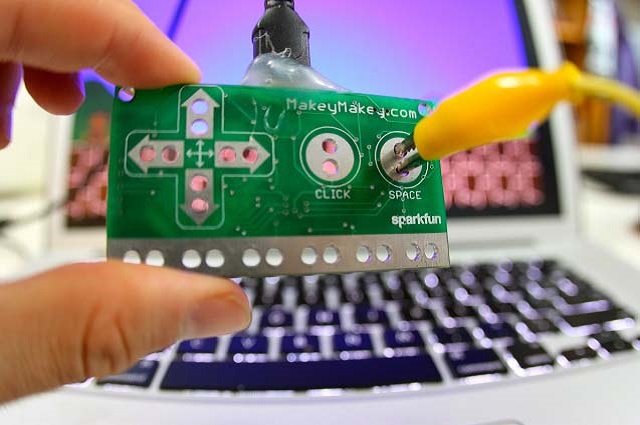
Investigating conductivity with Makey Makey boards
Students explore how electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits, using Makey Makey boards as the basis for experimentation and recoding of data.

Encryption of data is a means of protecting data, one example being the use of secret and public keys. This learning sequence examines cryptography and modern encryption methods for transmitting digital data securely.
Students explore different types of peripherals used every day to identify the data transmitted. A peripheral is an auxiliary device, such as a keyboard, that connects to and works with another device, for example a computer.
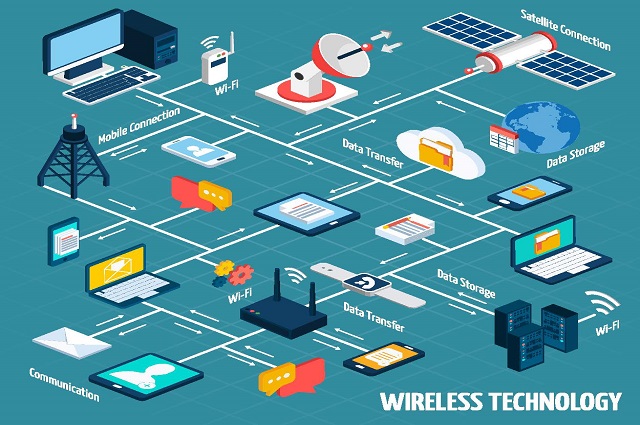
Through role-play and other activities, students develop understandings of the role of hardware and software in managing, controlling and securing the movement of and access to data in networked digital systems.
Computer chatter 1: Networks and data transmission
Using the concept of transportation systems as a comparison, students develop understandings of the properties of networked systems and the underlying techniques used to transmit and validate data.

Computer chatter 2: Network performance
Students build on and extend their knowledge of networks and discuss an inquiry question about wi-fi speeds and handling the bulk of data transfer needs.

In this sequence, students identify strengths and weaknesses of past, present and future methods of data storage. They also recognise the risks and benefits for users. Students explore specific 'data dilemmas'.

In this sequence students learn how the binary number system works and how we can represent text using binary numbers. They also learn one of the representations of the standard English alphabet used by computers. They look at how the same concepts apply to non-text data and analyse the effectiveness of some binary representation techniques to various types of data.
A teacher’s guide to the Intel Galileo
The Intel Galileo is a small, single-board computer designed for schools and hobbyists.
The Blueberry4™ is an educational computer kit with an accompanying support guide available for purchase.

Khan Academy: Meet the professionals
In these short case studies, professionals in computer science explain how they use their computer science and programming skills in their work.

