Programming LED circuit with Arduino IDE
About this lesson
Starting with a simple sequence of turning a LED on and off, the students can be challenged to choose a piece of music with a steady beat and program the lights to turn on and off in time to the music. This lesson idea was created by Toni Falusi.
Year band: 7-8
Curriculum Links AssessmentCurriculum Links
Links with Digital Technologies Curriculum Area
| Band | Content Description |
|---|---|
| 7-8 |
Design algorithms involving nested control structures and represent them using flowcharts and pseudocode (AC9TDI8P05). Trace algorithms to predict output for a given input and to identify errors (AC9TDI8P06). |
Assessment
Formative Assessment
- Observation of students creating initial circuit
- Review diagram sketch with students prior to connecting the components with alligator clips
- Successful upload & execution of external LED program
- Documentation of evidence of iteration of project, particularly changes made between the initial diagram sketch and the final product.
- Successful display of multiple blinking LED lights in alignment to the chosen music.
| Quantity of knowledge | Quality of understanding | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Criteria | Pre-structural | Uni-structural | Multi-structural | Relational | Extended abstract |
| Algorithms Programming |
Some attempt to copy the provided code into the program has been made. | Provided code has been copied into the program successfully . Limited customisatio n is evident. Eg. delay altered. |
Algorithm has been altered to change the sequence and timing of 2-5 external LED’s. Some instructions have been commented out in the program. |
Program has been extended to include 3-5 external LED’s. Attempt has been made to make LED’s flash to the beat of the chosen music. Algorithm has instructions commented out through the program. |
Algorithm brings in prior learning and/or independent learning beyond the task and possibly includes branching, variables and loops. Full use of Programming interface is evident |
| Diagram | Diagram contains all components of the project. Some evidence of labels. |
Complete diagram includes labels using correct vocabulary. Eg input/output, LED Some notation of of changes included. |
Diagram is complete, clearly labeled includes symbols and is easy to follow. Changes or iterations evident. | Specific vocabulary is used throughout the diagram. Proper symbols and explanation key is included. Iterations made during the project are documented. |
Correctly labelled diagram complete and presented to an excellent standard. Complete detail of all connections and hardware including description of components included. Iteration and changes documented, including a final reflection. |
| Vocabulary | No specific / technical terms used. | The terms program or code may be used as a general description. | The terms program or code are used as a general description. The terms analogue and digital are known and used correctly. |
Specific terms such as program, loop, debug are used confidently with specific reference to learner’s work. Code is commented in specific places. | Understanding of specific terms such as constant, function and variable. Understanding of terms in the code such as digitalWrite. Code is well commented throughout. |
Overview
Description
In this lesson students will be using components of the LilyPad development kit to create a circuit of LED’s that are controlled using a basic Arduino program, written in the Arduino IDE. Starting with a simple sequence of turning a LED on and off, the students can be challenged to choose a piece of music with a steady beat and program the lights to turn on and off in time to the music.
During the testing phase, the LilyPad components will be connected using alligator clips before progressing to hand stitching them together using conductive thread for a final product.
Resources
- Lilypad ProtoSnap kit with rechargeable battery
- LilyPad LED’s
- Conductive thread
- Alligator clips
- Arduino IDE installed onto computers
- Mini USB cable
- Chalk or pen for marking fabric
- Felt/Material
- Scissors
- Paper
- Needle
- Pencils for design sketches
- Embroidery hoop (suggested)
- Mac or PC with latest Arduino IDE installed:
For Windows
For Mac
Prior Student Learning
An understanding of basic circuitry is essential for this activity as it is important that the threads do not cross over or touch as you may short circuit the board.
Simple hand stitching skills would be beneficial but not essential as the components can be connected with alligator clips.
Learning hook
- Watch Youtube clip Frozen Christmas Lights (Let It Go)
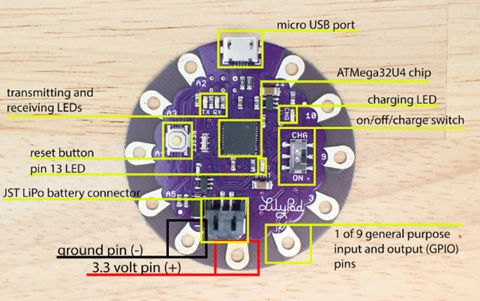
- Introduce the LilyPad kit, explaining the components - demonstrate a simple sequence by connecting the battery. Place alligator clip to the + on the microcontroller board and the + on LED. Connect second alligator clip to - on the board and LED. Turn switch to on to see the LED light up.
- Discuss port connections using alligator clips, and then conductive thread, highlighting the importance of ensuring the wires do not touch.
- Introducing the MicroController + Arduino provides a detailed description of the LilyPad components.
- Introduce the concept of functions and discuss how arduino has pre-defined functions for all the LilyPad components. Some of these functions include:
- loop - for repetition
- delay - delays action
- pinMode - for configuring the specified pin to behave either as an input or an output
- digitalWrite - for writing a low or high value to a pin
Learning map and outcomes
- Review basic electronics & circuitry.
- Explore Arduino IDE software that has been installed onto computers & configure port plus select Lilypad in Board Manager
- Upload basic LED blink program to Lilypad
- Connect LED to Lilypad port 5 and type code into Arduino to turn light on an off
- Create diagram flow chart to show connections needed for between 3-5 LEDs
- Students identify the ways in which their planned outcome can be decomposed into functions
- Students identify the key arduino functions and learn how to change parameters and use these these functions to achieve planned outcomes
- Create algorithm to sequence LED’s to turn on and off in a pattern of student’s choosing.
- Select appropriate piece of music and program LED’s to flash in a pattern that is reflective of the beat.
- Hand stitch Lilypad components onto fabric following the flow chart
- Present final project to the class.
Learning input
The teacher should have an understanding o
- circuitry,
- basic hand sewing techniques
- the elements of C language used in the Arduino IDE
- see Sew Electronics tutorial for programming your lilypad
Learning construction
- Students review knowledge of basic electronics and the issue of short circuits.
- Discuss concept of wearable technology. What is it? Why would it be useful?
- Introduce conductive thread discussing issues with insulation & resistance. The kit contains 2 ply thread that will compromise the brightness of the LED if sewn over a long distance. (This should not be a problem with this task)
- Open Arduino IDE and connect board to computer using mini USB cable
- Select the board type and port Tools_Board Manager_ LilyPad Arduino. Then Tools_port (select the serial port that is corresponds to the USB port eg:COM3
- Open example program in Arduino IDE File_Examples_01Basics_Blink. This program will turn the inbuilt LED on and off at one second (1000) intervals.
- Students can adapt the speed of the flashing by increasing the number eg 3000
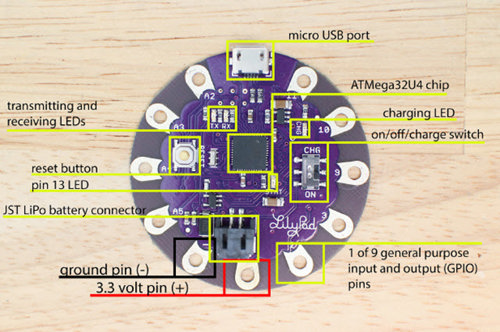
- Connect one LED to port 5 using the alligator clips from LilyPad port 5 to the + on the LED. Attach a second alligator clip to the Ground
- Type the following into the Arduino IDE:
#define LED1 5 //naming pin 5 as LED 1
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(LED1, OUTPUT); //initialise the digital pin as an output
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
digitalWrite(LED1,HIGH); //turn the LED on
delay (1000); //wait 1 second and do nothing digitalWrite
(LED1, LOW); //turn LED off
delay (1000); //wait another second and do nothing
- Upload the code to the Lilypad - Sketch_Upload
- Students write the pseudocode of this algorithm, focusing on how to decompose their algorithm into the key functions such as initializing the pins/board, writing a value to a pin and delaying.
- Identify the key blocks of the code, in particular the setup() and loop() functions, and discuss their purpose. What about the delay() function? What other functions of interest can students find?
- Introduce the notion of additional functions: for example, the code in the loop() can be a function in itself:
#define LED1 5 //naming pin 5 as LED 1
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(LED1, OUTPUT); //initialise the digital pin as an output
}
void lightLed(){
digitalWrite(LED1,HIGH); //turn the LED on
delay (1000); //wait 1 second and do nothing
digitalWrite(LED1, LOW); //turn LED off
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
lightLed();
delay (1000); //wait another second and do nothing
- Write the pseudocode of the desired algorithm, decomposing the outcome into key arduino functions and functions of their own.
- In groups, students test and debug their programs.
- As each additional LED is connected to the microcontroller - define each and add additional lines of code changing the name to LED2 LED3 etc.
- Choose music and students vary the delay and sequence of LED’s turning on and off to blink to the beat:
delay (500) //wait of half a second
** the shortest delay you can use is 1 as decimal numbers won't work. - Hand stitch all components to fabric following the flow chart.
Learning demo
- Students present their LED Music display to the class together with their sketch diagram.
Learning reflection
- Students reflect on their original diagram sketch and indicate any changes made between that and the final design.
- Is their design scalable? What are the limitations to the project? Eg. only 5 LED’s in the kit.
- Where might they market their final project if it was to be advertised and sold? Who would it appeal too?
- What challenges did they face? Eg: difficulty coding or sewing with the conductive thread. What changes could they make to their design or project to address these issues?
- Were they able to easily change existing code to produce a different outcome? What are the advantages/disadvantages of using functions in code?
- Did they discover an interesting/useful function they want to share?
Resources
- Download entire lesson plan
- Instructables: Let's Make with Lilypad - Website with additional ideas and instructions.
- Instructables: Wearable Electronics Class - Free online course teaching techniques to build wearable elecontronics and program interactions using Ardunio software. There are variances in the Lilypad kit supplied by CSER and those referred to in the lessons.